Schedule
Field Trip Information
Destination 1: Temperature by Free-Air CO2 Enrichment
An innovative new research platform known as T-FACE (Temperature by Free-Air CO2 Enrichment) established in Nanjing Municipality was developed by Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences to simulate climate change scenarios for the future (Fig. 1). This T-FACE not only enabled the air above open-field plots to be enriched with CO2, but also increased whole-ecosystem temperature (including water/soil, air and plant temperatures), for the entire growing season. For the elevated [CO2] treatment, the average daytime increase in [CO2] at crop canopy height was 200 ppm above the ambient conditions. The 1-min average of [CO2] was controlled to within 80% and 90% of the set point for 96% and 84% of the time, respectively. For the elevated temperature treatment, the daily increase in whole-ecosystem temperature was 2 °C above ambient conditions. The whole-ecosystem warming system created a quite uniform canopy temperature within the warmed plot (Fig. 2). The level of precision and stability achieved in the treatment control is of the first-class level.
This is the first T-FACE platform to explore the interaction between elevated [CO2] and whole-ecosystem warming in open ecosystems. The T-FACE systems allows plants to be exposure to [CO2] enrichment and whole-ecosystem warming under natural growth conditions, thus it can be used to assess the “actual” responses of plant and soil in the field. The T-FACE platform can provide climate change simulation conditions for crop science, soil science, plant nutrition, ecology, environmental science and other related fields. This enables the study of how farmland systems respond, adapt to and address climate change.

Fig. 1 Aerial view of the T-FACE platform in Nanjing Municipality.
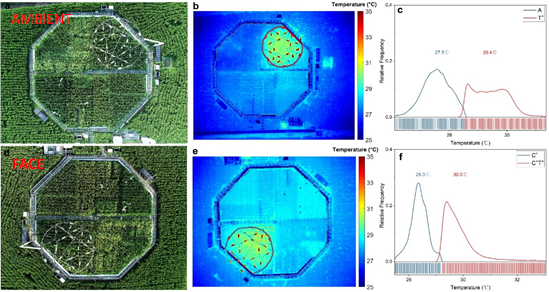
Fig. 2 (a) Picture of ambient CO2 plot, (b) Thermal image of the warming pattern in ambient CO2 plot, red circle stands for warmed plot, (c) Temperature variability for warmed plot (T+) and non-warmed plot (A) within ambient CO2 plot, (d) Picture of elevated CO2 plot, (e) Thermal image of the warming pattern in elevated CO2 plot, red circle stands for warmed plot, (f) Temperature variability for warmed plot (C+T+) and non-warmed plot (C+) within elevated CO2 plot.
Destination 2: Confucius Temple

Built as the site to worship the great Chinese thinker Confucius, the shrine known as Fuzi Miao in Chinese, has been the most bustling local cultural and commercial center since its establishment in 1034. Covering an area of 2.63 hectares with surrounding buildings in good harmony, it enjoys a typical architectural style from the Ming and Qing dynasties. (Source: nanjingtravel)
Learn More:
Destination 3: Zhonghua City-Gate
Named as ‘Treasure Gate’ in ancient times, it was the southern city-gate of Nanjing as the capital of the Ming Dynasty. It is marked by strict and regular layout of a unique structure, which is wrapped with iron on both sides with a groove cut inside for fastening the gate with a bolt. In the era of cold weapons, with the gate and the sluice closed right after enemy troops stormed into the city, they would be trapped in the enclosure. Inside the castle, there are 27 caves capable of hiding over 3,000 soldiers. This is a perfect symbol to reflect the construction and role of Nanjing as imperial center of government and power. (Source: nanjingtravel)